
Profits generally refer to the money a company earns after subtracting all costs and expenses from its total revenues. Yes, having high retained earnings is considered a positive sign for a company’s financial performance. Most software offers ready-made report templates, including a statement of retained earnings, which you can customize to fit your company’s needs. First, revenue refers to the total amount of money generated by a company.
How Net Income Impacts Retained Earnings

The net income (NI) is moved into retained earnings on the balance sheet as part of the closing entry process. The assumption is that all income from the company in one year is held for future use. The last closing entry reduces the amount retained by the amount paid out to investors. The expense accounts have debit balances so to get rid of their balances we will do the opposite or credit the accounts. Just like in step 1, we will use Income Summary as the offset account but this time we will debit income summary.
- Similarly, the iPhone maker, whose fiscal year ends in September, had $70.4 billion in retained earnings as of September 2018.
- They go up whenever your company earns a profit, and down every time you withdraw some of those profits in the form of dividend payouts.
- Retained Earnings (liability) are Credited (Cr.) when increased & Debited (Dr.) when decreased.
- Changes in unappropriated retained earnings usually consist of the addition of net income (or deduction of net loss) and the deduction of dividends and appropriations.
Revenue vs. Retained Earnings: What’s the Difference?
You should report retained earnings as part of shareholders’ equity on the balance sheet. The normal balance in a profitable corporation’s Retained Earnings account is a credit balance. This is logical since the revenue accounts have credit balances and expense accounts have debit balances.
Is Revenue More Important than Retained Earnings?
- Retained earnings are the portion of a company’s net income that management retains for internal operations instead of paying it to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- An accounting year-end which is not the calendar year end is sometimes referred to as a fiscal year end.
- As stated earlier, dividends are paid out of retained earnings of the company.
- These positive earnings can be reinvested back into the company and used to help it grow, but a significant amount of the profits are paid out to shareholders.
- We need to do the closing entries to make them match and zero out the temporary accounts.
- It is permanent because it is not closed at the end of each accounting period.
However, it can be challenged by the shareholders through a majority vote because they are the real owners of the company. There is an even more thorough formula to ensure that you have an accurate retained earnings end balance. Now, add the net profit or subtract the net loss incurred during the current period, that is, 2019.
Unit 14: Stockholders’ Equity, Earnings and Dividends

These funds are also held in reserve to reinvest back into the company through purchases of fixed assets or to pay down debt. At the end of each accounting period, businesses close out their revenue and expense accounts, summarizing them into a temporary account known as the Income Summary Account. The net balance (revenue – expenses) of this account is then transferred to Retained Earnings through closing entries. In essence, Retained Earnings represents the accumulated profits that a company has kept over time. This account is part of the Share Capital section of a company’s balance sheet and can be used for reinvestment in the business or to pay down debt.
This is the case where the company has incurred more net losses than profits to date or has paid out more dividends than what it had in the retained earnings account. The company cannot utilize the retained earnings until its shareholders approve it. Thus, retained earnings are credited to the books of accounts when increased and debited when decreased. If the balance of retained earnings is negative, then it is referred to as accumulated losses/deficit, or retained losses.
- The Retained Earnings account can be negative due to large, cumulative net losses.
- When the Retained Earnings account has a debit balance, a deficit exists.
- Profit is the total income earned from sales of goods and services and is considered the bottom line for companies.
- Let’s look at the stockholders’ equity section of a balance sheet for a corporation that has issued only common stock.
- Finally, the closing balance of the schedule links to the balance sheet.
- For example, company A which is a trading company has a net income of $25,000 which all of its respective income and expenses have already been transferred to the income summary account at the end of 2020.
Drawings Accounts and Closing Journals

Retained earnings are the residual net profits after distributing dividends to the stockholders. It reconciles the beginning balance of net income or loss for the period, subtracts dividends paid to shareholders and provides the ending balance of retained earnings. HP Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1. The company decided to retain the earnings for that year and utilize them for further growth. This is a liability (shareholders’ fund) of the company to pay the earnings back to the shareholders.
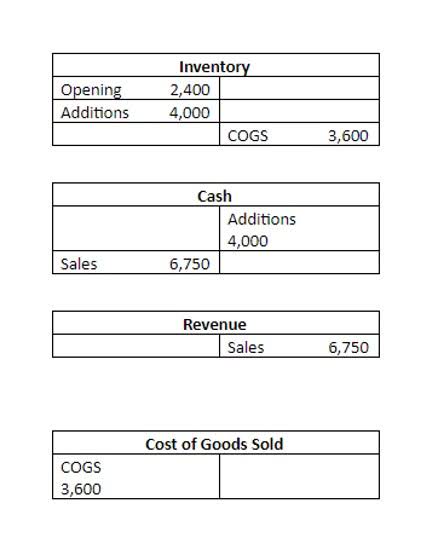
Also, this outflow of cash would lead to a reduction in the retained earnings of the company as dividends are paid out of retained earnings. There is no requirement for companies to issue dividends on common shares of stock, although companies may try to attract investors by paying yearly dividends. Stock dividends are payments made in the form of additional shares paid out to investors. Revenue on the income statement is often a focus for many stakeholders, but the impact of a company’s revenues affects the balance sheet. If the company makes cash sales, a company’s balance sheet reflects higher cash balances.
Management and Retained Earnings
These expenses often go hand-in-hand with the manufacture and distribution of products. For example, a company may pay facilities costs for its corporate headquarters; by selling products, the company hopes to pay its facilities costs and have money left over. Even though some refer to retained earnings appropriations as retained do you debit or credit retained earnings earnings reserves, using the term reserves is discouraged. Generally speaking, the par value of common stock is minimal and has no economic significance. However, if a state law requires a par (or stated) value, the accountant is required to record the par (or stated) value of the common stock in the account Common Stock.

